NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING
- Liquid Penetrate Inspection
- Magnetic Particle Inspection
Liquid Penetrate Inspection:
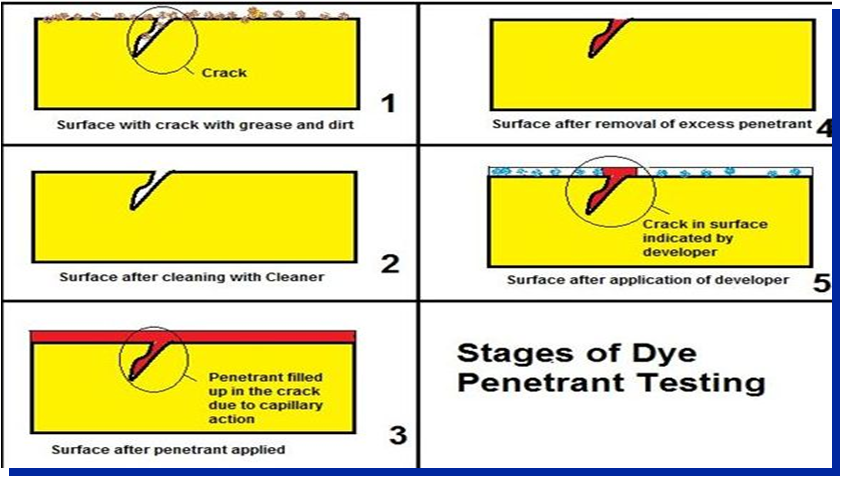
Liquid penetrate is an NDT method that utilizes the principle of capillary action in which liquid of suitable physical properties can penetrate deep into extremely fine cracks or pitting that are opened to the surface without being affected by the gravitational force.
Advantages :-
- Simple to perform
- Inexpensive
- Applicable to materials with complex geometry
Limitation :-
- Limited to detection of surface breaking discontinuity
- Not applicable to porous material
- Require access for pre- and post-cleaning
- Irregular surface may cause the presence of non-relevant indication
Magnetic Particle Inspection:
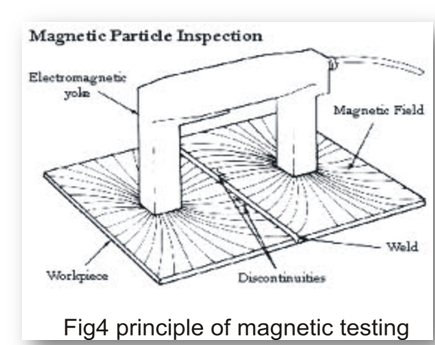
Magnetic particle testing (MT) is a NDT method that utilizes the principle of Magnetization.
Material to be inspected is first magnetized through one of many ways of magnetization.
Once magnetized, a magnetic field is established within and in the vicinity of the material.
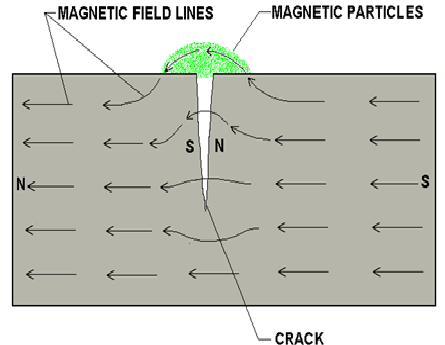
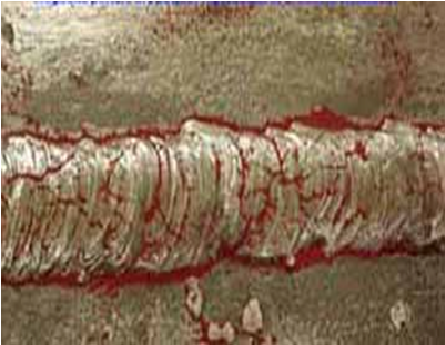
Finely milled iron particles coated with a dye pigment are then applied to the specimen. These magnetic particles are attracted to magnetic flux leakage fields and will cluster to form an indication directly over the discontinuity.
They provide a visual indication of the flaw.
The presence of surface breaking and subsurface discontinuity on the material causes the magnetic field to ‘leak’ and travel through the air.
Such a field is called ‘leakage field’. When magnetic powder is sprayed on such a surface the leakage field will attract the powder, forming a pattern that resembles the shape of the discontinuity.
This indication can be visually detected under proper lighting conditions
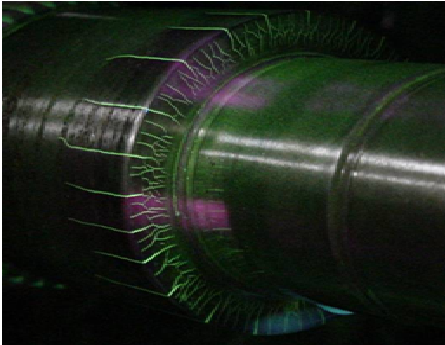
Examples of visible dry magnetic particle indications
Indication of a crack in a saw blade
Indication of cracks in a weldment
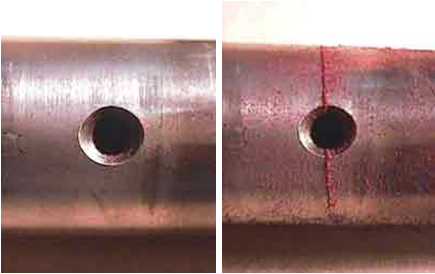
Before and after inspection pictures of cracks emanating from a hole
Indication of cracks running between attachment holes in a hinge
Advantages :-
- Inexpensive
- Equipment are portable
- Equipment easy to operate
- Provide instantaneous results
- Sensitive to surface and subsurface discontinuities
Limitations :-
- Applicable only to ferromagnetic materials
- Insensitive to internal defects
- Require magnetization and demagnetization of materials to be inspected
- Require power supply for magnetization
- Material may be burned during magnetization
- Introduction to NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING NDT
- Overview of Six Most
- Common NDT Methods
- Principle, Working & Application
INTRODUCTION:
- What is NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING NDT ?
The use of noninvasive techniques to determine the integrity of a material, component or structure or quantitatively measure some characteristic of an object.
i.e. Inspect or measure without doing harm.
What are Some Uses of NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING NDT Methods:
- Flaw Detection and Evaluation
- Leak Detection
- Location Determination
- Dimensional Measurements
- Structure and Microstructure Characterization
- Estimation of Mechanical and Physical Properties
- Stress (Strain) and Dynamic Response Measurements
- Material Sorting and Chemical Composition Determination
When are NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING NDT Methods Used?
There are NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING NDT application at almost any stage in the production or life cycle of a component.
–To assist in product development
–To monitor, improve or control manufacturing processes
–To verify proper processing such as heat treating
–Fatigue and Creep damage prediction
–To inspect fitness-for-service evaluation
Major types of NON DESTRUCTIVE TESTING NDT:
- Detection of surface flaws
- Visual
- Magnetic Particle Inspection
- Fluorescent Dye Penetrant Inspection
- Detection of internal flaws
- Radiography
- Ultrasonic Testing
- Eddy current Testing