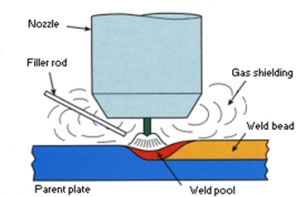
WELDING PROCESS
RESPONSIBILITIES OF A WELDING ENGINEER
BEFORE WELDING:
- REVIEWING OF DRAWINGS AND SPECIFICATIONS
- CHECKING OF QUALIFICATION OF PROCEDURES TO BE USED
- REVIEWING OF MATERIALS TO BE USED (WELDING CONSUMABLE, SHIELDING GAS, BACKING, etc)
- CHECKING OF SURFACE CLEANLINESS
- CHECKING FITUP AND ALIGNMENT OF WELD JOINTS
DURING WELDING:
- PREHEAT TEMPERATURE
- QUALITY OF ROOT BEAD
- INTERPASS TEMP.
- SEQUENCE OF WELD PASS
- INTER PASS CLEANING
- CONFORMANCE TO APPLICABLE PROCEDURE (VOLTAGE, CURRENT, HEAT INPUT AND TRAVEL SPEED)
AFTER WELDING:
- POST HEATING
- FINAL WELD APPEARANCE
- PRESENCE OF DISCONTINUITIES
- POST WELD HEAT TREATMENT
- AMOUNT OF DISTORTION
WELDING:
- Welding joins two pieces of metal / material by the use of heat, pressure, or both
- Brazing or soldering involves a filler metal which has a lower melting point than the metal pieces to be joined
- Metal cutting is done by heating the metal with a flame and directing a stream of pure oxygen along the line to be cut
COMMON WELDING PROCESSES:
1.SHIELDED METAL ARC WELDING
2.SUBMERGED ARC WELDING
3.GAS TUNGSTEN ARC WELDING
4.FLUX CORED ARC WELDING
CODES, STANDARDS AND SPECIFICATIONS TO BE FOLLOWED FOR FABRICATION:
- ASME
- SEC. IX FOR WELDING PROCEDURE SPECIFICATION
- SEC. IIC FOR WELDING CONSUMABLE SELECTION
- SEC.IIA FOR FERROUS METAL SPECIFICATION
- SEC.VIII FOR PRESSURE VESSEL FABRICATION
- EN 288 FOR WPS QUALIFICATION & EN 287 FOR WPQ.
- IBR
MANUFACTURING PRODUCTS:
I) HEADERS: V) COILS:
WATER WALL HEADER 1. ECONOMISER COIL
SUPER HEATER HEADER 2. SUPER HEATER COIL
REHEATER HEADER 3. EVAPOURATOR COIL
ECONOMISER HEADERS 4. BED SUPER HEATER
DRAIN HEADERS
II) DRUM:
HP DRUM
LP DRUM
STEAM DRUM
III) STORAGE TANK
IV) DEAERATOR
WPS & PQR:
Welding Procedure Specification:
It is a written document that provides direction to the welder for making production welds in accordance with code requirements.
Any WPS must be qualified by the manufacturer.
WPS specifies the condition (ranges) under which welding must be performed called variables.
WPS addresses essential, supplementary essential and non essential variables
Purpose of WPS Qualification:
To determine that the weldment is capable of providing the required properties for the intended application.
WPS establishes the properties of the weldment and not the skill of the welder.
Procedure Qualification Record:
It documents what occurred during welding the test coupon and the results of the test coupon.
PQR documents the essential variables and other specific information and the results of the required testing. In addition, when notch toughness is required for procedure qualification, the applicable supplementary essential variables shall be recorded.
Procedure Qualification:
PQR is a record of welding data to weld a test coupon. It also contains test results.
Completed PQR shall document all essential variables including ranges.
PQR to be certified accurate and shall not be subcontracted.
If more than one process then weld deposit thickness for each process and filler metal to be recorded.
Weld Orientation:
Plate groove positions 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G
Pipe groove positions 1G, 2G, 5G, 6G
Plate fillet positions 1F, 2F, 3F, 4F
Pipe fillet positions 1F, 2F, 2FR, 4F, 5F
1F – 0 to 30
2F – +15 -10 wrt 45
4F – 0 – 125
3F – 125 – 235
Base Metal Classification:
P nos depend on composition, weldability & mechanical properties.
Group nos classify metals within P nos for procedure qualification where notch toughness requirements are specified. But base metals can not be indiscriminately substituted.