RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING
RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
Radiographic testing is based on the principle of radiation emitted by high energy short wave length electro magnetic wave spectra.
SOURCES OF RADIATION IN RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
- Particulate radiation – α & β,
- Electromagnetic radiation X & γ.
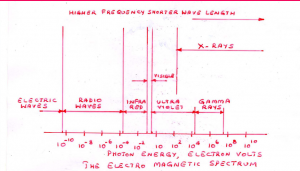
ELECTRO MAGNETIC SPECTRUM:
 X & γ RAYS RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
X & γ RAYS RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
X and Gamma rays comprise the high energy, short wavelength portion of the Electro magnetic wave spectrum. Throughout the spectrum, X and Gamma rays have the same characteristics. X and Gamma rays of the same wave length have identical properties.
STEPS INVOLVED IN RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
- 1. Clean the object.
- 2. Subject the object to VT for any surface irregularities.
- 3. Attach the film to the object along with the applicable IQI (Image Quality Indicator).
- 4. Expose the film.
- 5. Develop the film.
- 6. View the film.
- 7. Record the observations.
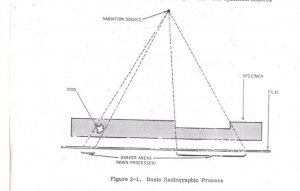
PROCESS OF RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
GAMMA RAY CAMERA:
FILM LOADED IN CASSETTE:
FILM IN RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
- Silver salts suspended in an emulsion coated on a transparent cellulose acetate or nitrate base with protective gelatin coating.
FILM ATTACHED TO COMPONENT:
The silver salts are acted upon by Radiation. The intensity of of the reaction in the emulsion is directly proportional to the amount of radiation received which depends upon the specimen configuration and defects if any.
DEVELOPER:
Alkaline. 21 Deg C.
Changes the exposed silver salts to black metallic silver.
5 to 8 minutes.
STOP BATH:
ACIDIC 21 DEG C
Neutralizes the developer and stops the developing process.
1 to 2 minutes
FIXING:
ACIDIC 21 DEG C
Continues neutralization. Dissolves unexposed silver salts allowing them to fall from film. Hardens (tans) the film.
5 to 15 minutes.
WASHING:
Clean running water. 21 Deg C.
Hourly flow 4 to 8 times tank volume. Removes all chemicals.
10 to 30 minutes.
Twice fixing time.
WETTING:
Aerosol solution.
Eliminates most water spots and streaks.
0.5 to 1 minute.
DRYING:
Warm filtered circulating air dries the film.
30 to 45 minutes.
VIEWING THE FILM:
 TECHNIQUES IN RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
TECHNIQUES IN RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
- Single wall single image technique.
- Double wall single image technique.
- Double wall double image technique.
- Superimposing technique.
- Latitude technique.
APPLICATION OF RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
- Both X- Rays and Gamma Rays can be used for radiographic testing.
- Applicable to variety of materials irrespective of the size and shape.
- Very little surface preparation of the object is required in radiographic testing.
- In the radiographic testing film is a permanent record.
- Interpretation is very easy in radiographic testing since a photographic image of the discontinuity is obtained.
LIMITATIONS OF RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING:
- Safety is the biggest concern in radiographic testing.
- Affects the work progress, since the area is to be cordoned off to prevent personnel getting exposed to radiation.
- In case of Gamma ray, the source has to be sent back to the facility for irradiation.
To Learn RADIOGRAPHIC TESTING Kindly Contact Us…